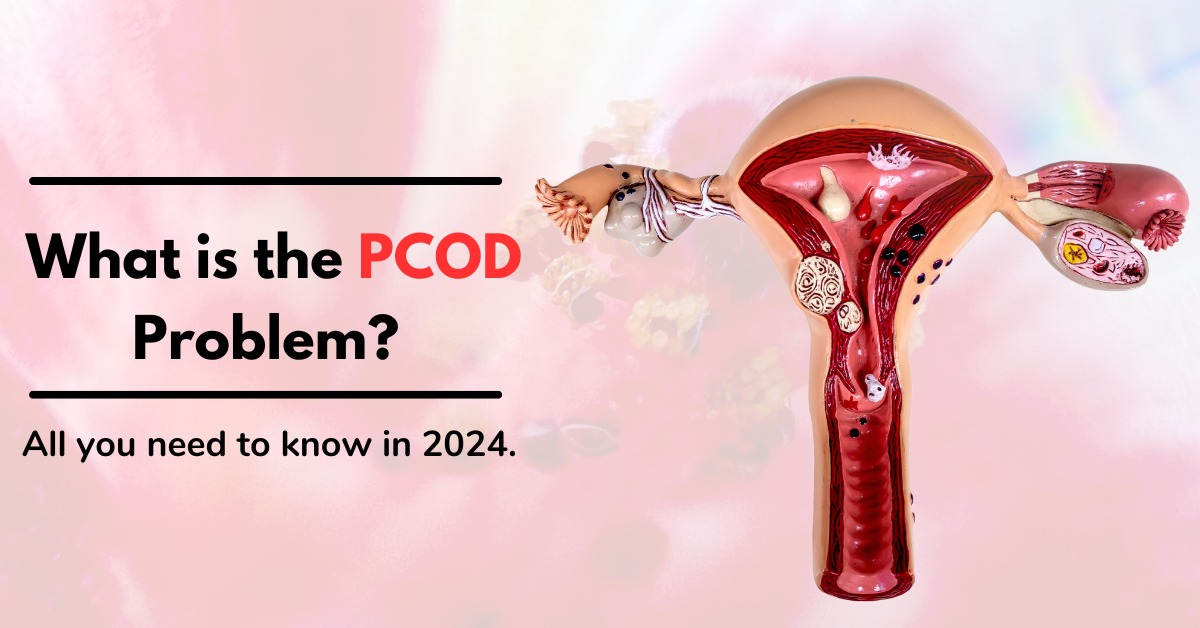
What is the PCOD problem? All you need to know in 2024.
The PCOD problem
Understanding the Complexities of this Common Hormonal Disorder: Poly-cystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), often referred to as PCOD (poly-cystic ovary disorder), is a prevalent hormonal disorder affecting women worldwide. PCOD problem arises from various factors, including genetic predisposition, hormonal imbalances, and lifestyle factors. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the intricate details of the PCOD problem, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and management strategies.
Introduction
In women, PCOD problem arises from the development of cysts in the ovaries, disrupting their normal function. This results in an imbalance of hormones, particularly an excess of male hormones. Consequently, hormonal disturbances affect menstruation and fertility, among other issues. Women affected by PCOD problems often experience irregular or prolonged menstrual cycles, accompanied by elevated levels of androgen. Moreover, the ovaries may form numerous small fluid-filled sacs (follicles) and fail to release eggs regularly.
If left unaddressed, PCOD problems can lead to more severe complications like heart disease and diabetes. To gain a comprehensive understanding of the PCOD problem and its implications, continue reading below.
Understanding the PCOD Problem
PCOD problem is characterized by a range of symptoms, stemming from hormonal imbalances and metabolic irregularities. Women with PCOD problems may experience irregular menstrual cycles, ovarian cysts, excessive hair growth (hirsutism), acne, and weight gain, among other manifestations. These symptoms can significantly impact a woman’s physical health, emotional well-being, and fertility.

Causes of the PCOD Problem
The exact cause of the PCOD problem remains elusive, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors. Genetic predisposition plays a role, as PCOD problem often runs in families. Hormonal imbalances, including elevated levels of androgens (male hormones) and insulin resistance, contribute to the development of PCOD problems. Lifestyle factors such as poor diet, lack of exercise, and stress can also exacerbate symptoms.
- Hormonal Imbalance: PCOD problems often stem from an imbalance in hormones, including increased levels of male hormones like testosterone.
- Genetic Factors: Genetic predisposition plays a role, as PCOD problem tends to run in families.
- Insulin Resistance: Many women with PCOD problems also experience insulin resistance, where the body’s cells don’t respond effectively to insulin.
- Lifestyle Factors: Poor diet, lack of exercise, and high-stress levels can contribute to the development of PCOD problems.
- Inflammation: Chronic inflammation in the body may also be a contributing factor to PCOD problems.
- Environmental Influences: Exposure to certain environmental pollutants and toxins may increase the risk of developing PCOD problems.
Symptoms of PCOD Problem
Recognizing the symptoms of PCOD problems is crucial for early detection and intervention. Common symptoms include irregular menstrual cycles, infertility, acne, hair loss or thinning, weight gain, and mood swings. Women with PCOD problems may also experience pelvic pain, oily skin, and darkening of the skin in certain areas, such as the neck and armpits.
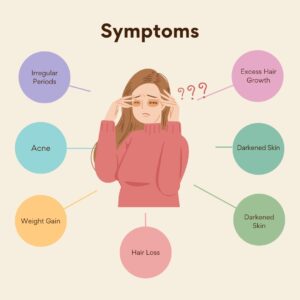
- Irregular Periods: Menstrual cycles may be unpredictable or infrequent.
- Excess Hair Growth: Unwanted hair on the face, chest, or back.
- Acne: Persistent breakouts, often on the face, chest, or back.
- Weight Gain: Difficulty losing weight or unexplained weight gain.
- Hair Loss: Thinning hair or bald patches on the scalp.
- Darkened Skin: Patches of darkened skin, especially in skin folds.
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness or lack of energy.
- Mood Swings: Fluctuations in mood, ranging from irritability to depression.
- Difficulty Getting Pregnant: Trouble conceiving due to irregular ovulation.
- Pelvic Pain: Discomfort or pain in the lower abdomen or pelvis.
Diagnosing PCOD Problem
Diagnosing PCOD problems involves a comprehensive evaluation of medical history, symptoms, and diagnostic tests. Medical history may reveal irregular menstrual cycles, infertility, or other symptoms indicative of the PCOD problems. Physical examination may reveal signs such as acne, hirsutism, or enlarged ovaries. Diagnostic tests, including blood tests to assess hormone levels, and ultrasound imaging to visualize the ovaries, and rule out other conditions, help confirm the diagnosis of PCOD problem.

- Medical History: Reviewing symptoms and menstrual patterns.
- Physical Examination: Assessing signs like acne and hirsutism.
- Hormone Tests: Checking levels of hormones like testosterone.
- Ultrasound: Imaging ovaries to detect cysts or follicles.
- Rule Out Other Conditions: Excluding similar disorders like thyroid problems.
- Comprehensive Evaluation: Combining tests for accurate diagnosis.
Treatment Strategies for PCOD Problem
Managing the PCOD problem requires a multifaceted approach aimed at addressing symptoms and underlying hormonal imbalances. Lifestyle modifications such as adopting a healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress management techniques can help improve symptoms and promote overall well-being. In some cases, surgical interventions such as ovarian drilling or assisted reproductive technologies may be recommended to address infertility.

- Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a healthy diet and regular exercise routine.
- Medications: Prescribing oral contraceptives to regulate menstrual cycles.
- Anti-androgen Medications: Addressing symptoms like acne and hirsutism.
- Fertility Treatments: Assisting with ovulation through medications like clomiphene.
- Weight Management: Supporting weight loss to improve hormone levels.
- Surgery: Consider procedures like ovarian drilling in certain cases.
Challenges of Living with PCOD Problem
Living with the PCOD problems can present various challenges, both physical and emotional. Women with PCOD problems may struggle with infertility, weight management, acne, and other symptoms that impact their quality of life. Managing these challenges requires patience, perseverance, and support from healthcare providers, family, and friends.

- Fertility Struggles: Difficulty conceiving due to irregular ovulation.
- Emotional Impact: Managing stress, anxiety, and depression associated with PCOD.
- Weight Management: Challenges in maintaining a healthy weight due to hormonal imbalances.
- Hormonal Symptoms: Coping with acne, hirsutism, and other visible manifestations.
- Long-term Health Risks: Addressing increased risk of conditions like diabetes and heart disease.
Individuals with PCOD problems must address these complications through appropriate medical care and lifestyle management.
Support and Resources for Women with PCOD Problems
Support and resources are available to help women navigate the complexities of the PCOD problem. Support groups, online forums, and educational resources provide valuable information, encouragement, and a sense of community for women living with the PCOD problems. Healthcare providers, including gynecologists, endocrinologists, and fertility specialists, play a crucial role in diagnosing, managing, and supporting women with PCOD problems.

- Healthcare Providers: Consult gynecologists, endocrinologists, and fertility specialists for expert guidance.
- Support Groups: Join online or in-person support groups to connect with others facing similar challenges.
- Educational Resources: Access reliable information through books, websites, and reputable organizations specializing in PCOD.
- Mental Health Services: Seek counseling or therapy to address emotional well-being and coping strategies.
- Community Outreach: Engage with community health programs or workshops offering support and resources for women with PCOD problems.
Empowering Women to Take Control of Their Health
Empowering women to take control of their health is essential in managing PCOD problems. Education, advocacy, and self-care are key components of empowering women with PCOD problems to advocate for themselves, make informed decisions about their health, and access appropriate medical care and support services.
- Education: Provide access to comprehensive information about PCOD, its causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
- Encouragement: Foster a supportive environment that empowers women to advocate for their health needs and make informed decisions.
- Access to Healthcare: Ensure women have access to affordable and quality healthcare services, including regular check-ups and screenings.
- Support Networks: Establish support groups or online communities where women can share experiences, seek advice, and offer encouragement.
- Self-care Practices: Promote self-care activities such as regular exercise, stress management techniques, and healthy lifestyle habits to empower women to prioritize their well-being.
Conclusion
The PCOD problem is a complex hormonal disorder that affects millions of women worldwide. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for PCOD problems, women can take proactive steps to manage their health and well-being effectively. With the support of healthcare providers, family, and community, women with the PCOD problems can navigate the challenges they face and lead fulfilling lives.
FAQs
1. What is the main reason for PCOD?
The primary cause of the PCOD problems is believed to be a combination of genetic predisposition, hormonal imbalances, particularly elevated androgen levels, and insulin resistance, contributing to irregular ovulation and other symptoms.
2. What happens if a girl has PCOD?
If a girl has a PCOD problem, she may experience irregular menstrual cycles, infertility due to irregular ovulation, excessive hair growth (hirsutism), acne, weight gain, and hormonal imbalances. PCOD problems can also increase the risk of developing conditions like diabetes, heart disease, and endometrial cancer if left untreated.
3. Can a PCOD girl get pregnant?
Yes, a girl with the PCOD problems can still get pregnant, although it may be more challenging due to irregular ovulation. With appropriate medical management, lifestyle changes, and sometimes fertility treatments, many women with PCOD problems can conceive and have successful pregnancies.
4. How can I improve my PCOD?
To improve the PCOD problem, focus on lifestyle changes such as maintaining a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management. Medications may also be prescribed to regulate menstrual cycles and hormone levels. Consulting with a healthcare provider is essential for personalized treatment and management strategies.
5. Can PCOD be cured?
The PCOD problems cannot be cured, but they can be effectively managed through lifestyle changes, medications, and other interventions. With proper treatment and ongoing care, many women with PCOD problems can experience symptom relief and improve their overall health and well-being.
Also Read:
How to Get Periods Immediately to Avoid Pregnancy: Quick and Effective Methods.
https://myblogpod.com/category/nutrient-rich-recipes-for-wellness/
References:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459251/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9964744/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4433074/
Disclaimer: What is the PCOD Problem? All You Need to Know in 2024
This article provides general information about PCOD (Polycystic Ovarian Disorder). It is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Please consult a healthcare provider for diagnosis and treatment. We are not responsible for any health outcomes.



One thought on “What is the PCOD problem? All you need to know in 2024.”
A informative blog.